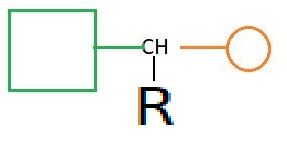
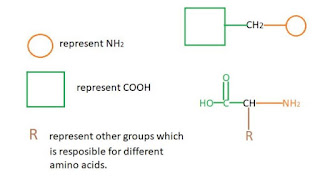
Cause of chemical shifts (ll)
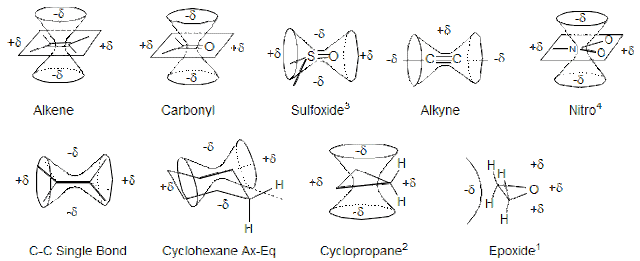
Other Factors affecting Chemical shifts. · One is Inductive effect which was stated earlier (in previous post). · Hybridisation of C atom: This is somehow related to inductive effect. There are generally three types of hybridisation of carbon observed in organic compounds( sp3 sp2 and sp). We know that more the ‘s’ character more will be the deshielding (more ‘s’ character shows availability of electron cloud towards more to the nucleus) and more will be chemical shift. According to above , the order of chemical shift will be: sp > sp2 > sp3 but this is not actual order , the order is : sp2 > sp3 > sp This trend is explained by another term called Magnetic Anisotropy. · Magnetic Anisotropy: The word anisotropy means non spherical environment. For example let us take a C-C single bonded carbon atom. When we see the electron clou...